Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
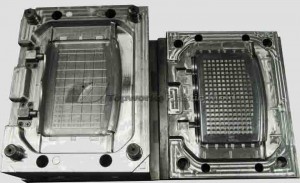
it is necessary first to explain what a mold is expected to do. Throughout this article, we use the term “molds” to indicate any device used to provide the final shape and dimensional details of a product. A mold is only one item in a series of devices that act to shape a plastics material. The vast majority of molds are made up essentially of two halves which open and close.
One half of the mold is called the plunger or core, and is known as the male half of the mold. The other half is called the cavity, and is known as the female half of the mold. Obviously then, the male half forms the inside of a part, whereas, the female half forms the outside contour of a part.
The raw material that is to be molded is an end product of some other organization. There are separate companies that specialize in resins, fillers,mould components. The final mate-from many different components combined in accordance with a “recipe” and processed through very precise chemical and mechanical processes. The chemical reaction processes are not within the province of this text. Reference should be made to the Glossary to gain familiarity with materials.
There are books avaiiable on each of the components, processes and devices. We will make effort to tell you how to develop and operate a chemical process, or how to build and operate a press. However, the designing of a mold is closely related to the equipment that will be used for the mold to operate in desired fashion. Regardless of the process used, some kind of a mold ls required if the end product is to be formed into the specified shape.
This device, called a mold, can range from a simple wooden or plaster form to a very complicated and extremely large (10 or 20 ton) mechanism.

The extremely simple molds of wood and plaster are usually used by the hobbyist who wants to experiment.Plastics Mold Engineering will not be able to cover everything. This prelude to basic types and features will give you an initial understanding of the molds only.That enterprising persons have put together to make a fascinating device that probably will do a job previously considered impossible.
Our point here is—The most complicated mold ever built was made up of the simple components and the texture described in this text. Most inventions are simply the application of known engineering principles to a new problem, the result being a device or method to lighten man’s work, reduce his effort to achieve a wanted goal, or reach his goal in shorter time.
The primary function of a mold is to shape the finished product. In order to do this it must have some means of introducing the plastics material to be formed; it must have some means of forming the inside, outside, and both sides of the product; it must have some means of maintaining the temperature desired in the process; it must have some external or internal mechanism for operating the various features of the mold; it must have some means for allowing the finished product to be removed from the sections which were used in the forming process (this is called ejection)’, after ejection, it must provide for easy removal of any and all excess material that may have been left during the previous cycle; it must be designed and constructed with adequate strength in the various sections to resist the alternate application and release of pressure.
All plastics processing requires three elements, in varying proportions, depending upon the processing characteristics of the material to be molded or processed. These three elements are time, temperature, and pressure. Time ranges from fractions of a second to hours, or days. Temperature ranges are from freezing to 1200 or 1500°F (650-815° Celsius). Pressure ranges are from negative (vacuum) to 50,000 psi.
The purpose of this particular statement is to show the impossibility of detailing or mentioning every contingency that may be encountered. In this chapter, we will show examples of the basic mold features and the different types that can be used in any combination that will perform the job required by the mold. First we will discuss press operation,second, general mold types and, finally,mold construction features.
Using these three elements, an engineer should be able to convey to a designer precisely what is to be designed. A good designer will make a rough sketch or preliminary layout to determine the various wall thicknesses, runner layouts (the path the material will-take.into the mold), and the features that he wishes to have incorporated into mold.
Before proceeding with a description of the specific mold types and fea-tures,it would be well to discuss the press and operations of the mold in the press in order to understand just what function the mold plays in the process of plastics fabrication.